MLA CITATION
The MLA (Modern Language Association) citation style is commonly used in the humanities, particularly in literature, language studies, and the arts. It emphasizes authorship and provides a straightforward method for citing sources. MLA citations consist of two main components: in-text citations and a Works Cited page.
1. In-Text Citations
In MLA style, in-text citations are brief references within your text. They direct the reader to the full citation in the Works Cited list. The in-text citation typically includes the author's last name and the page number from which the information was taken.
Format:
- (Author's Last Name Page Number)
Examples:
-
For a paraphrase:
(Smith 45)
According to Smith, technological advancements have revolutionized education (45). -
For a direct quote:
"The rise of technology has reshaped modern learning environments" (Smith 45).
If the source has two authors, both last names are included:
(Smith and Johnson 45)
For three or more authors, use the first author's last name followed by "et al.":
(Smith et al. 45)
If you mention the author's name in the sentence, include only the page number in parentheses:
Smith argues that technology has revolutionized education (45).
2. Works Cited
The Works Cited page appears at the end of your document and provides full details for each source cited in the text. Entries are arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name and include core elements such as the author's name, title of the source, and publication information. The MLA style uses a hanging indent for each entry, where the first line is aligned with the left margin, and subsequent lines are indented.
Core Elements of MLA Citation:
The basic structure of an MLA citation is composed of the following elements, as applicable:
- Author.
- Title of the source.
- Title of the container (e.g., book, journal, website).
- Other contributors (e.g., editors, translators).
- Version (e.g., edition).
- Number (e.g., volume and issue numbers).
- Publisher.
- Publication date.
- Location (e.g., page range, URL, DOI).
These elements are typically followed by a period and listed in this specific order.
Examples for Different Sources:
Books:
In-text citation:
- (Smith 45)
Works Cited entry:
- Format:
Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of the Book. Publisher, Year of Publication.
Example:
Smith, John. The Evolution of Technology. HarperCollins, 2020.
Journal Articles:
In-text citation:
- (Brown 34)
Works Cited entry:
- Format:
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of the Article." Title of the Journal, vol. number, no. number, Year, pages. Database/Website Name, DOI or URL.
Example:
Brown, Emily. "The Influence of Social Media on Mental Health." Journal of Psychology, vol. 12, no. 3, 2019, pp. 34-45. JSTOR, https://doi.org/10.1234/jpsy.2019.234.
Websites:
In-text citation:
- (Johnson)
Works Cited entry:
- Format:
Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of the Webpage." Title of the Website, Publisher, Date of Publication, URL. Accessed Day Month Year.
Example:
Johnson, Patricia. "The Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture." The Environmental Blog, 10 April 2020, www.environmentalblog.com/climate-change-agriculture. Accessed 15 July 2022.
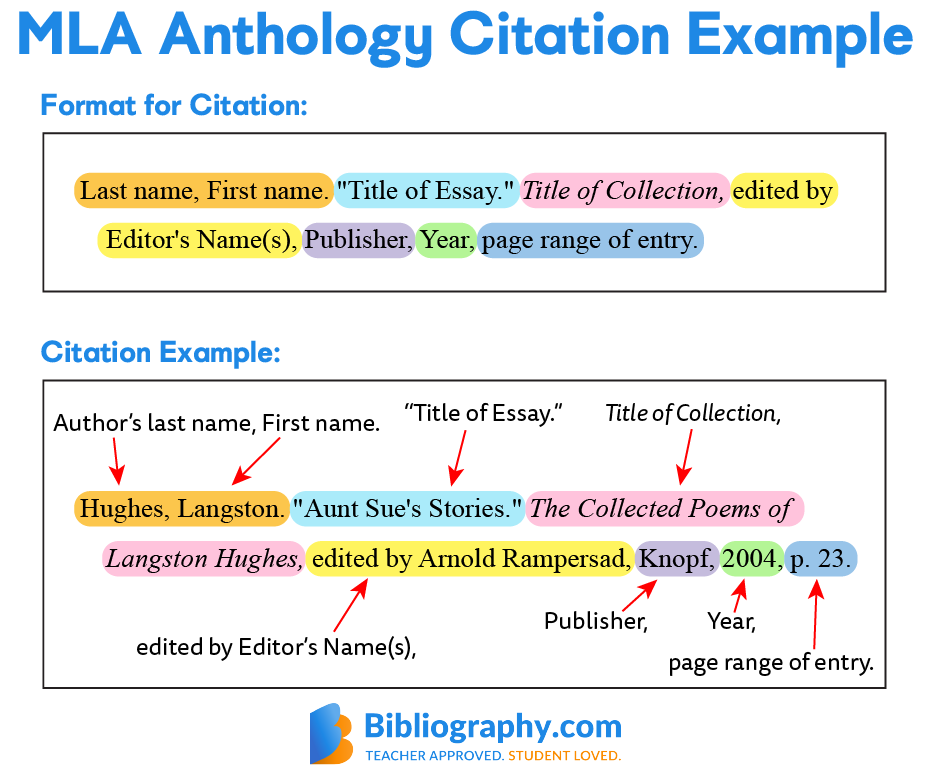
Chapters in Edited Books:
In-text citation:
- (Roberts 50)
Works Cited entry:
- Format:
Chapter Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of the Chapter." Title of the Book, edited by Editor's First and Last Name, Publisher, Year, pages.
Example:
Roberts, A. "New Advances in AI." Technology and Innovation in the 21st Century, edited by Paul Green, Tech Press, 2021, pp. 50-75.
3. Key Features of MLA Style:
- Author-Page System: MLA style uses the author’s last name and the page number for in-text citations.
- Works Cited Page: This is a comprehensive list of all sources cited in your paper. It is arranged alphabetically by the authors' last names.
- Hanging Indent: Every entry in the Works Cited page uses a hanging indent, where the first line is flush with the left margin, and subsequent lines are indented.
- Title Capitalization: In MLA, the titles of sources are capitalized, with the first word, the last word, and all major words capitalized (called "title case").
4. Special Cases in MLA Citation
- No Author: If a source has no author, the title of the work appears in the in-text citation and at the beginning of the Works Cited entry.
In-text citation:
("The Impact of Technology" 45)
Works Cited entry:
"The Impact of Technology on Education." Tech Publishers, 2020.
-
Multiple Authors: For sources with two authors, both names are listed in the in-text citation and Works Cited. For three or more authors, "et al." is used after the first author's name.
-
Containers: Many sources are part of a larger whole (like a journal article within a journal, or a webpage within a website). MLA requires you to acknowledge the larger "container" in your citation, such as the book title for a chapter or the website name for an article.
5. Why Use MLA Citation?
MLA citation is well-suited for disciplines that require detailed analysis of texts, such as literature, philosophy, and the arts. It provides a clear and consistent method for attributing sources, which helps avoid plagiarism, enhances the credibility of your work, and allows readers to locate your references easily.
The simplicity of MLA’s author-page system makes it easy to integrate into your writing, and the structured Works Cited page ensures that all sources are properly credited.